 |
| DC Source |
Let us see some basic of AC and
DC voltage sources and their use. All the cell and battery are
source of DC voltage source. DC stands for Direct Current. In a DC voltage
source, the voltage is uniform and do not change with time, it remain constant.
Mostly all the devices around us at home run on DC supply.
The 220C AC supply is
reduced to lower voltage like 5V, 12V, 24V etc using step down transformer and then converted to DC voltage using Diode which we will learn in next post. Other
battery operated devices directly take DC from cell or battery used in it like
toys, wall clocks, mobile phones etc. You can see in the voltage & time
graph above, the colored straight lines indicate different voltage graphs which are
constant w.r.t time axis; Red one is for 3V supply similarly Blue for 1V, Light Green for -2.5V and the Purple line for
-4V.
Similarly the main supply coming
in our home from electricity department is AC
 |
| AC Source |
supply which is 220V in India and
110V in other countries. In AC supply the voltage keeps on changing with time
and it can follow any trend of variation with time.
In this diagram I have
shown a voltage changing smoothly with time, this type of curve is called Sinusoidal
wave which we study in trigonometry. We can see at t=0 the curve starts from ‘0’
and at time=2, it reaches peak value and then slopes down to zero at t=4. This
is positive cycle as the voltage from t=0 to t=4 is in positive quadrant of
graph. Next the curve move forward in negative direction from t=4 onward and
reaches negative peak at t=6 and again reverse back to zero at t=8. Hence the
curve between t=4 to t=8 is negative cycle as it is in negative quadrant.
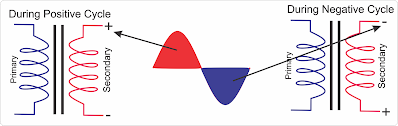 |
| Polarity Change |
These means the AC supply changes
its polarity, once it is in positive cycle one of the terminal is ‘+’ and other
is ‘-‘, but for the next negative cycle the polarity reverses as we can see in
the diagram. Though I have shown total time for one positive and one negative
cycle as 8secs, but in case of our home AC supply, this duration is actually
20milli second also denoted as 20ms (1Sec = 1000mSec).
That means positive half
cycle of AC supply at our home completes in half this time that is 10ms and
rest negative half in 10ms and the cycle goes on. As we know relation between
time period and frequency is T = 1/For F=1/T, where ‘T’ in seconds and ‘F’ in
Hertz or Hz. So in our case F = 1/20ms = 1000/20 = 50Hz. So in India the AC
supply is 220V and 50Hz. But in other countries AC supply is 110V and 60Hz, so
if frequency is high the time period is low as per formula T=1/F, hence
positive and negative cycles are completed faster in foreign countries i.e. 1/60Hz
= 0.01666 Sec = 16.66ms as compared to 20ms in India.
 |
| Sample Rating of an Adapter |
So, if you see the rating of any
laptop or mobile charger or any other electrical equipment, it will be
mentioned as 220V/50Hz so it will work in India only or if it is mentioned as
110V/60Hz it will work outside India, if it is connected at our home supply, it
will burn as you are providing supply of 220V which is double its rating
i.e.110V. Now a day, most of the electronics equipment is designed to work on
both supply voltage i.e. starting from 110V to 230V and 50 to 60Hz as we can
see on modern devices, one of which is shown here for reference.
That’s all about AC and DC supply
basic, next we will learn about diodes and then will make a small circuit using
transformer, diode and capacitor.







0 Comments